Python3 条件控制
Python 条件语句是通过一条或多条语句的执行结果(True 或者 False)来决定执行的代码块。
可以通过下图来简单了解条件语句的执行过程:
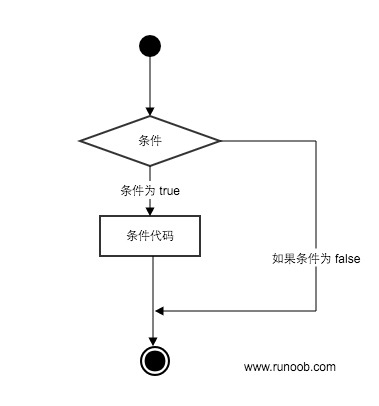
代码执行过程:
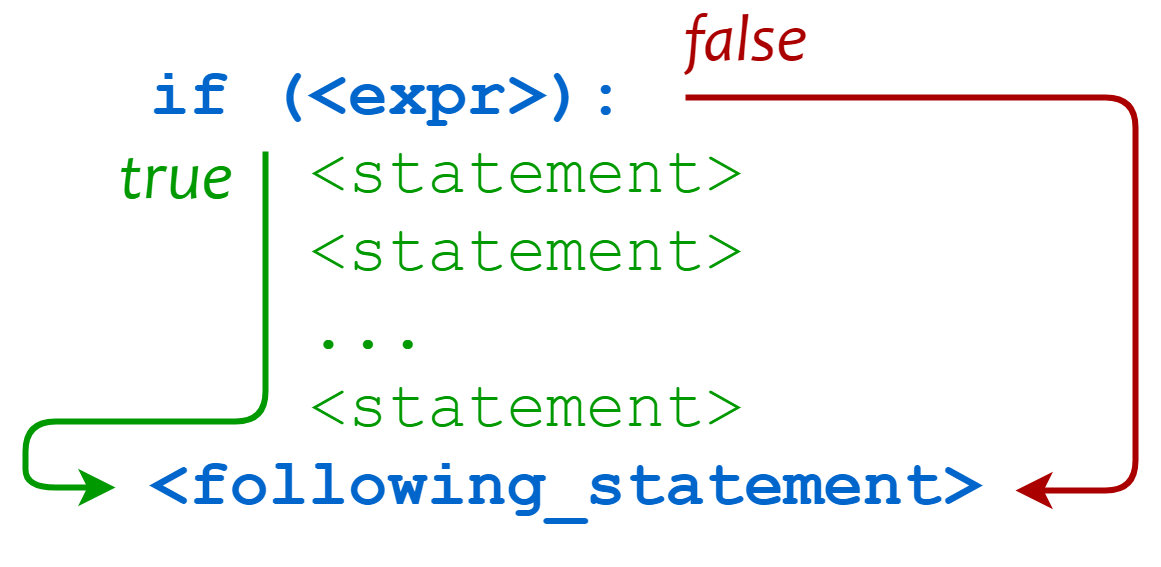
if 语句
Python中if语句的一般形式如下所示:
if condition_1:
statement_block_1
elif condition_2:
statement_block_2
else:
statement_block_3
- 如果 "condition_1" 为 True 将执行 "statement_block_1" 块语句
- 如果 "condition_1" 为False,将判断 "condition_2"
- 如果"condition_2" 为 True 将执行 "statement_block_2" 块语句
- 如果 "condition_2" 为False,将执行"statement_block_3"块语句
Python 中用 elif 代替了 else if,所以if语句的关键字为:if – elif – else。
注意:
- 1、每个条件后面要使用冒号 :,表示接下来是满足条件后要执行的语句块。
- 2、使用缩进来划分语句块,相同缩进数的语句在一起组成一个语句块。
- 3、在 Python 中没有 switch...case 语句,但在 Python3.10 版本添加了 match...case,功能也类似,详见下文。
Gif 演示:

实例
以下是一个简单的 if 实例:
实例
#!/usr/bin/python3
var1 = 100
if var1:
print ("1 - if 表达式条件为 true")
print (var1)
var2 = 0
if var2:
print ("2 - if 表达式条件为 true")
print (var2)
print ("Good bye!")
执行以上代码,输出结果为:
1 - if 表达式条件为 true 100 Good bye!
从结果可以看到由于变量 var2 为 0,所以对应的 if 内的语句没有执行。
以下实例演示了狗的年龄计算判断:
实例
#!/usr/bin/python3
age = int(input("请输入你家狗狗的年龄: "))
print("")
if age <= 0:
print("你是在逗我吧!")
elif age == 1:
print("相当于 14 岁的人。")
elif age == 2:
print("相当于 22 岁的人。")
elif age > 2:
human = 22 + (age -2)*5
print("对应人类年龄: ", human)
### 退出提示
input("点击 enter 键退出")
将以上脚本保存在dog.py文件中,并执行该脚本:
$ python3 dog.py 请输入你家狗狗的年龄: 1 相当于 14 岁的人。 点击 enter 键退出
以下为if中常用的操作运算符:
| 操作符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
< |
小于 |
<= |
小于或等于 |
> |
大于 |
>= |
大于或等于 |
== |
等于,比较两个值是否相等 |
!= |
不等于 |
实例
#!/usr/bin/python3
# 程序演示了 == 操作符
# 使用数字
print(5 == 6)
# 使用变量
x = 5
y = 8
print(x == y)
以上实例输出结果:
False False
high_low.py文件演示了数字的比较运算:
实例
#!/usr/bin/python3
# 该实例演示了数字猜谜游戏
number = 7
guess = -1
print("数字猜谜游戏!")
while guess != number:
guess = int(input("请输入你猜的数字:"))
if guess == number:
print("恭喜,你猜对了!")
elif guess < number:
print("猜的数字小了...")
elif guess > number:
print("猜的数字大了...")
执行以上脚本,实例输出结果如下:
$ python3 high_low.py 数字猜谜游戏! 请输入你猜的数字:1 猜的数字小了... 请输入你猜的数字:9 猜的数字大了... 请输入你猜的数字:7 恭喜,你猜对了!
if 嵌套
在嵌套 if 语句中,可以把 if...elif...else 结构放在另外一个 if...elif...else 结构中。
if 表达式1:
语句
if 表达式2:
语句
elif 表达式3:
语句
else:
语句
elif 表达式4:
语句
else:
语句
实例
# !/usr/bin/python3
num=int(input("输入一个数字:"))
if num%2==0:
if num%3==0:
print ("你输入的数字可以整除 2 和 3")
else:
print ("你输入的数字可以整除 2,但不能整除 3")
else:
if num%3==0:
print ("你输入的数字可以整除 3,但不能整除 2")
else:
print ("你输入的数字不能整除 2 和 3")
将以上程序保存到 test_if.py 文件中,执行后输出结果为:
$ python3 test.py 输入一个数字:6 你输入的数字可以整除 2 和 3
match...case
Python 3.10 增加了 match...case 的条件判断,不需要再使用一连串的 if-else 来判断了。
match 后的对象会依次与 case 后的内容进行匹配,如果匹配成功,则执行匹配到的表达式,否则直接跳过,_ 可以匹配一切。
语法格式如下:
match subject:
case <pattern_1>:
<action_1>
case <pattern_2>:
<action_2>
case <pattern_3>:
<action_3>
case _:
<action_wildcard>case _: 类似于 C 和 Java 中的 default:,当其他 case 都无法匹配时,匹配这条,保证永远会匹配成功。
实例
def http_error(status):
match status:
case 400:
return "Bad request"
case 404:
return "Not found"
case 418:
return "I'm a teapot"
case _:
return "Something's wrong with the internet"
mystatus=400
print(http_error(400))
以上是一个输出 HTTP 状态码的实例,输出结果为:
Bad request
一个 case 也可以设置多个匹配条件,条件使用 | 隔开,例如:
...
case 401|403|404:
return "Not allowed"
match...case 更多内容参考:Python match-case 语句


小奈
734***009@qq.com
以下实例 x 为 0-99 取一个数,y 为 0-199 取一个数,如果 x>y 则输出 x,如果 x 等于 y 则输出 x+y,否则输出y。
#!/usr/bin/python3 import random x = random.choice(range(100)) y = random.choice(range(200)) if x > y: print('x:',x) elif x == y: print('x+y:', x + y) else: print('y:',y)小奈
734***009@qq.com
kein
201***63.com
#!/usr/bin/python3 """对上面例子的一个扩展""" print("=======欢迎进入狗狗年龄对比系统========") while True: try: age = int(input("请输入您家狗的年龄:")) print(" ") age = float(age) if age < 0: print("您在逗我?") elif age == 1: print("相当于人类14岁") break elif age == 2: print("相当于人类22岁") break else: human = 22 + (age - 2)*5 print("相当于人类:",human) break except ValueError: print("输入不合法,请输入有效年龄") ###退出提示 input("点击 enter 键退出")kein
201***63.com
阿科
121***125@qq.com
数字猜谜游戏优化
print('二、数字猜谜游戏') print('数字猜谜游戏!') a = 1 i = 0 while a != 20: a = int (input ('请输入你猜的数字:')) i += 1 if a == 20: if i<3: print('真厉害,这么快就猜对了!') else : print('总算猜对了,恭喜恭喜!') elif a < 20: print('你猜的数字小了,不要灰心,继续努力!') else : print('你猜的数字大了,不要灰心,继续加油!')阿科
121***125@qq.com
小叶
shi***0415@163.com
#!/usr/bin/python3 # 继续扩展,加入用户提示判断是否退出还是继续 print("=======欢迎进入狗狗年龄对比系统========") control = "N" while control=="N": try: age = int(input("请输入您家狗的年龄:")) #print(" ") age = float(age) if age < 0: print("您在逗我?") elif age == 1: print("相当于人类14岁") #break elif age == 2: print("相当于人类22岁") #break else: human = 22 + (age - 2)*5 print("相当于人类:",human) #break except ValueError: print("输入不合法,请输入有效年龄") print("") control = input("退出(Y/N)?") print("") ###退出提示 input("点击 enter 键退出")小叶
shi***0415@163.com
米老鼠
468***534@qq.com
条件为假:0, false, '', None, 例子如下:
条件为真:不为 0, True, 'None', 字符串不为空串
米老鼠
468***534@qq.com
JIECAO
shi***lingmail@vip.qq.com
使用判断语句来实现 BMI 的计算。
BMI 指数(即身体质量指数,简称体质指数又称体重,英文为 Body Mass Index,简称BMI),是用体重公斤数除以身高米数平方得出的数字
#!/usr/bin/env python3 print('----欢迎使用BMI计算程序----') name=input('请键入您的姓名:') height=eval(input('请键入您的身高(m):')) weight=eval(input('请键入您的体重(kg):')) gender=input('请键入你的性别(F/M)') BMI=float(float(weight)/(float(height)**2)) #公式 if BMI<=18.4: print('姓名:',name,'身体状态:偏瘦') elif BMI<=23.9: print('姓名:',name,'身体状态:正常') elif BMI<=27.9: print('姓名:',name,'身体状态:超重') elif BMI>=28: print('姓名:',name,'身体状态:肥胖') import time; #time模块 nowtime=(time.asctime(time.localtime(time.time()))) if gender=='F': print('感谢',name,'女士在',nowtime,'使用本程序,祝您身体健康!') if gender=='M': print('感谢',name,'先生在',nowtime,'使用本程序,祝您身体健康!')JIECAO
shi***lingmail@vip.qq.com
babeimi
xia***i3941@hotmail.com
参考地址
下表列出了不同数值类型的 true 和 false 情况:
babeimi
xia***i3941@hotmail.com
参考地址
Yuanlgone
183***68730@163.com
if 的两种格式:
可以括号限定代码域,加强代码可读性。
name ="pag" if name == "pag": print(name=="pag") # True if (name == "pag"):{ print(name == "pag") # True }Yuanlgone
183***68730@163.com
存在时间
tsj***o@qq.com
取随机数扩展。取随机数直到两数相等,显示取数次数。
import random x = random.choice(range(100)) y = random.choice(range(100)) b,c = x,y a = 1 print(x,y) while x != y: if x > y: print('x:',x) elif x == y: print('x+y:', x + y,'totall cal ',a,'times') else: print('y:',y) x = random.choice(range(100)) y = random.choice(range(100)) a = a+1 print('initialized data:',b,c,'x+y:', x + y,'total cal ',a,'times')存在时间
tsj***o@qq.com
川河岳
cit***ai@qq.com
存在时间 楼上的太复杂了,而且 elif 还不会执行到,优化如下:
import random a = 0 while True: x = random.choice(range(100)) y = random.choice(range(100)) a = a+1 if x > y: print(x,'>',y) elif x < y: print(x,'<',y) else: print('x=y=', x, 'total cal ', a, 'times') break川河岳
cit***ai@qq.com
葫芦又
111***0177@qq.com
如果 if 语句中的条件过长,可以用接续符 \ 来换行。
例如:
if 2>1 and 3>2 and 4>3 and \ 5>4 and 6>5 and 7>6 and \ 8>7: print("OK")注意: \ 后的一行要缩进没有要求,可无序缩进,但我们保持代码的可读性一般设置同样的缩进格式。
葫芦又
111***0177@qq.com
秋 | 先生
mas***lipeng@163.com
实例:
# 查询 n 到 m 间的所有素数 def find_prime_number(n, m): if isinstance(n, int) and isinstance(m, int): if m <= 1: return "error range" if 1 >= n > m: return "error start" numbers = list() num = n while num <= m: i = 2 while i < num: if (num % i == 0) and (num != i): break else: i += 1 if num == i: numbers.append(num) num += 1 return numbers else: return "error input" print(find_prime_number(1, 100))秋 | 先生
mas***lipeng@163.com
My_Skity
719***459@qq.com
在 if...elif...else 的多个语句块中只会执行一个语句块,例如:
age = int(input("请输入你家狗狗的年龄: ")) print("") if age <= 0: print("你是在逗我吧!") elif 1 <= age <=2: #与下一个elif条件重复,只执行符合条件的第一个语句块 print("相当于 14 岁的人。") elif age == 2: print("相当于 22 岁的人。") elif age > 2: human = 22 + (age - 2) * 5 print("对应人类年龄: ", human)因此,在写 elif 条件时一定要做到互不重复。
My_Skity
719***459@qq.com
洋洋涵
wan***ngdh2015@126.com
模式匹配
match ... case 是 Python 3.10 中引入的一个新特性,也被称为“模式匹配”或“结构化匹配”。
它为 Python 带来了更强大、更易读的分支控制,相比于传统的 if-elif-else 链。
基本模式匹配
x = 10 match x: case 10: print("x is 10") case 20: print("x is 20") case _: print("x is something else")在这里,_是一个特殊的“占位符”模式,用于匹配任何值(类似于 else)。
序列模式匹配
point = (2, 3) match point: case (0, 0): print("Origin") case (0, y): print(f"Point is on the Y axis at {y}") case (x, 0): print(f"Point is on the X axis at {x}") case (x, y): print(f"Point is at ({x}, {y})") case _: print("Not a point")对象模式匹配
class Point: def __init__(self, x, y): self.x = x self.y = y p = Point(0, 3) match p: case Point(x=0, y=y): print(f"Point is on the Y axis at {y}") case Point(x=x, y=0): print(f"Point is on the X axis at {x}") case Point(x, y): print(f"Point is at ({x}, {y})") case _: print("Not a point")OR 模式
使用 | 来表示一个或多个模式。
x = 2 match x: case 1 | 2 | 3: print("x is 1, 2, or 3") case _: print("x is something else")守卫
你可以使用 if 在模式匹配中添加额外的条件。
x = 10 match x: case x if x > 5: print("x is greater than 5") case _: print("x is 5 or less")洋洋涵
wan***ngdh2015@126.com